Describe the Structure of the Bladder
The urinary system has two parts. The bladder divideS into two.
In our entire urinary system series the urinary bladder and.

. Histologically the urinary bladder is lined with transitional epithelium and does not produce mucus. The size and position of lower urinary structures vary with male and female anatomy. Anatomy of the Bladder.
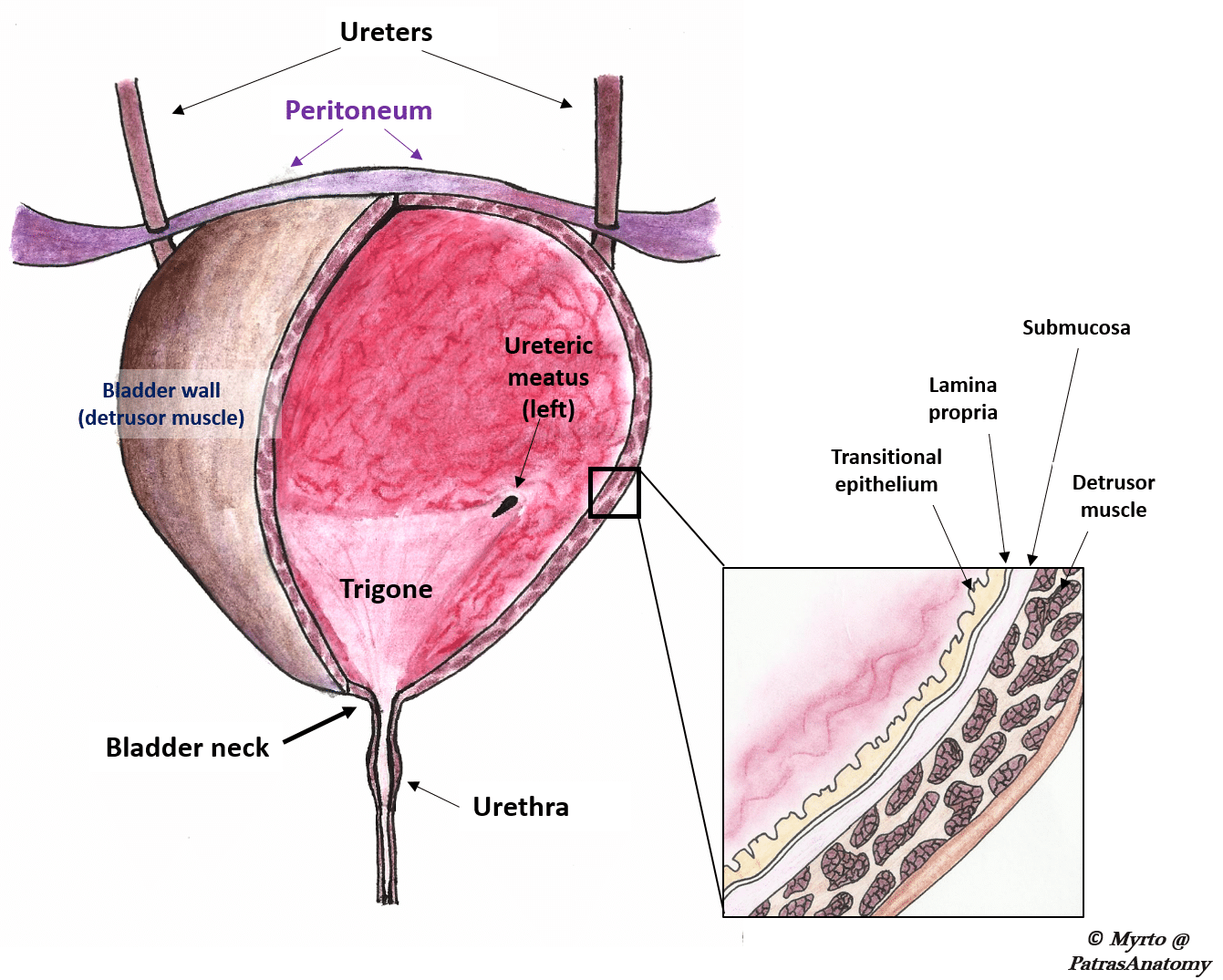
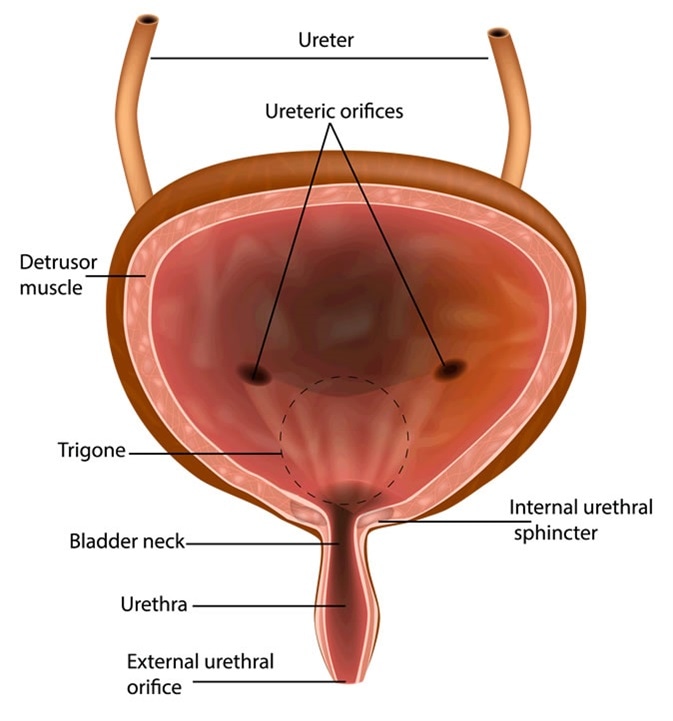
They filter blood and remove waste from the body in the form of urine. Kidneys Filter Blood at the Top of the Urinary System. Fundus base which contains the trigone.
The urinary bladder and urethra are pelvic urinary organs whose respective functions are to store and expel urine outside of the body in the act of micturition urination. Urethra Function and Structure. Describe the structure of the urinary bladder.
The urinary bladder is a muscular sac in the pelvis just above and behind the pubic bone. It is one of the most elastic organs of the body and is able to increase its volume greatly to accommodate between 600 to 800 ml of urine at maximum capacity. Men and women have the same upper urinary tract but their lower urinary tracts are different.
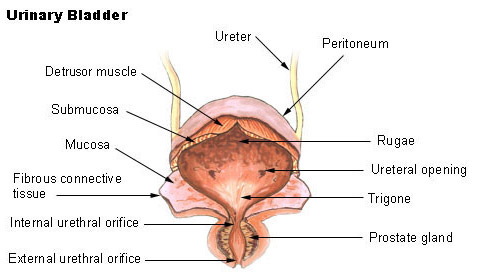
It controls and delays the process. Unlike the female urethra the male urethra is a structure shared between the urinary and reproductive systems. It has a folded internal lining known as rugae which allows it to accommodate up to 400-600ml of urine in healthy adults.
Provide sensation and motor control of urination. The bladder like the stomach is an expandable saclike organ that contracts when it is empty. The size and shape of the urinary bladder varies with the amount of urine it contains and with the pressure it receives from surrounding organs.
The male urethra extends from the bladder passing through the. It is located in the pelvic cavity posterior to the symphysis pubis and below the parietal peritoneum. Upon examination specific landmarks are used to describe the location of any irregularities in the bladder.
It is located in the extraperitoneal space of the pelvis behind the pubic bones and extends into the abdomen when filled with urine. As is the case with most of the pelvic viscera there are differences between male and female anatomy of the urinary bladder and urethra. Explain micturition reflex and describe how it controls the voiding of urine.
The urethra is a thin tube that connects to the bladder in order to empty urine out of the body. The urethra is held closed by the urethral sphincter a muscular structure that helps keep urine in the bladder until voiding can occur. This article will describe the anatomy of the urinary bladder.
It is a hollow and elastic organ which stores the urine produced by the kidneys. 1Mucosanumerous folds 2Muscular layer has 3 distinctives layers of smooth muscle Serosa superiorly outermost layer. The bladders walls relax and expand to store urine and contract and flatten to empty urine through the urethra.
From the bladder urine is excreted through a tube called the urethraIn women this tube is about 15 inches long and exits the body at the upper aspect of the vaginal opening. 1 The male urethra not only carries urine out of the bladder but it also transports semen. The urinary bladder functions as a storage vessel for urine to delay the frequency of urination.
The typical healthy adult bladder can store up to two cups of urine for two to five hours. The urinary bladder is a sac that serves as a reservoir for urine. Trigone which houses the urethra.
The urinary bladder is a temporary storage reservoir for urine. The empty bladder is about the size and shape of a pear. The bladder is an organ of the urinary system.
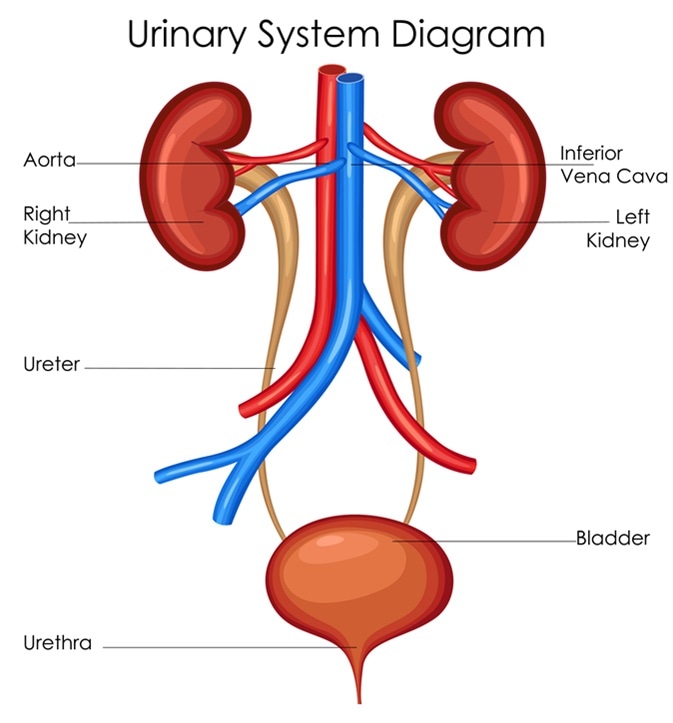
In females the main urethra functions are the transportation of urine out of the body prevention of urine reflux and protection against pathogenic bacteriaIn males the urethra has four functions the expulsion of urine the expulsion of sperm the prevention of either of these fluids from traveling back into the lower. It is located in the lower pelvic cavity. This urine produced by the kidneys flows via the ureters in to the bladder.
The lower urinary tract contains the bladder and the urethra. Describe the functional anatomy of ureters urinary bladder and male and female urethra. The urinary bladder is a hollow muscular organ in the abdominal cavity situated on the pelvic region that acts to store and release urine into.
The upper urinary tract and the lower urinary tract. After its full the urine passes through the urethra and exits the body. The bladder is the next structure on the journey where the ureters empty the urine.
The female urethra is short about 15 inches long while the male urethra is longer at 7 to 8 inches in length as it runs length of the penis. Urine drains from the kidneys into the bladder through the ureters. Transitional epithelium elastic fibers and visceral muscle tissue in the walls of the.
Describe the structure of the urethra Urethra duct that transmits urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body during urination. It plays two main roles. A urinary bladder functions as the bodys storage tank for urine.
The urine formed by the nephrons of the kidneys is transported to the urinary bladder for storage before it gets expelled through the urethra. It is a hollow distensible muscular organ. Body which collects the urine.
Temporary storage of urine - the bladder is a hollow organ with distensible walls. Together the two kidneys and two ureters make up the upper urinary tract. When empty the bladder is about the size and shape of a pear.
Kidneys filter the blood producing urine that is stored in the bladder prior to elimination through the urethra. It serves as a holding reservoir for urine until you are. The inner lining of the bladder tucks into the folds and expands out to accommodate liquid.
Modification of work by NCI The kidneys illustrated in Figure 1 are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below and posterior to the liver in the peritoneal cavity. The adrenal glands sit on top of each. The kidneys ureters bladder and urethra are the primary structures of the urinary system.
What are the basic layers that form the structure of the urinary bladder.

Urine Transport And Other Structures Of The Urinary System Anatomy And Physiology
The Urinary Bladder Structure Function Nerves Teachmeanatomy
No comments for "Describe the Structure of the Bladder"
Post a Comment